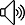LVM 是 Logical Volume Manager( 邏輯卷管理器 ) 的簡寫,它為主機(jī)提供了更高層次的磁盤存儲管理能力。 LVM 可以幫助系統(tǒng)管理員為應(yīng)用與用戶方便地分配存儲空間。 在 LVM 管理下的邏輯卷可以按需改變大小或添加移除 。另外, LVM 可以為所管理的邏輯卷提供定制的命名標(biāo)識。因此,使用 LVM 主要是方便了對存儲系統(tǒng)的管理,增加了系統(tǒng)的擴(kuò)展性。
Linux , AIX , Hp-uinx 平臺下的 LVM 命令是不一樣的。下面以 Redhat 下的命令來做一些說明。
一 . LVM 理論知識
1. 先來看一下 LVM 創(chuàng)建的流程: PV-->VG-->LV.
PV(Physical Volume) :物理卷, 可以是單獨(dú)磁盤,也可以是硬盤分區(qū)。
VG(Volume Group) :卷組, 是 PV 的組合,可以看成單獨(dú)的邏輯磁盤。
LV(Logical Volume) :邏輯分區(qū), 當(dāng)于物理分區(qū)的 /dev/hdaX ,只有邏輯卷才可以寫數(shù)據(jù)。
PE(Physical Extent) :物理范圍。 VG 單元,類似于 RAID 的條帶大小。 當(dāng)多個 PV 組成一個 VG 時, LVM 會在所有 PV 上做類似格式化的動作,將每個 PV 切成一塊塊的空間, 這一塊塊的空間就稱為 PE, 通常是 4MB 。
LE(Logical Extent) :邏輯范圍。 LV 的組成單位。 大小為 PE 的倍數(shù) ( 通常為 1:1) 。
2. 工作原理
LVM 在每個物理卷頭部都維護(hù)了一個 metadata ,每個 metadata 中都包含了整個 VG 的信息,包括每個 VG 的布局配置、 PV 的編號、 LV 的編號,以及每個 PE 到 LE 的映射關(guān)系。同一個 VG 中的每個 PV 頭部的信息是相同的,這樣有利于故障時進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)恢復(fù)。
LVM 對上層文件系統(tǒng)提供 LV 層,隱藏了操作細(xì)節(jié)。對文件系統(tǒng)而言,對 LV 的操作與原先對 Partition 的操作沒有差別。當(dāng)對 LV 進(jìn)行寫入操作時, LVM 定位相應(yīng)的 LE ,通過 PV 頭部的映射表,將數(shù)據(jù)寫入到相應(yīng)的 PE 上。
LVM 實(shí)現(xiàn)的關(guān)鍵在于在 PE 和 LE 間建立映射關(guān)系,不同的映射規(guī)則決定了不同的 LVM 存儲模型。 LVM 支持多個 PV 的 Stripe 和 Mirror ,這點(diǎn)和軟 Raid 的實(shí)現(xiàn)十分相似。
使用 LVM 的優(yōu)勢:
?文件系統(tǒng)可以跨多個磁盤,因此大小不會受物理磁盤的限制。
?可以在系統(tǒng)運(yùn)行狀態(tài)下動態(tài)地?cái)U(kuò)展文件系統(tǒng)大小。
?可以增加新磁盤到 LVM 的存儲池中。
?可以以鏡像的方式冗余重要數(shù)據(jù)到多個物理磁盤上。
?可以很方便地導(dǎo)出整個卷組,并導(dǎo)入到另外一臺機(jī)器上。
使用 LVM 的限制:
?在從卷組中移除一個磁盤時必須使用 reducevg ,否則會出問題。
?當(dāng)卷組中的一個磁盤損壞時,整個卷組都會受影響。
?不能減小文件系統(tǒng)大小(受文件系統(tǒng)類型限制)。
?因?yàn)榧尤肓祟~外的操作,存儲性能會受影響(使用 Stripe 的情況另當(dāng)別論)。
二 . 創(chuàng)建相應(yīng)的磁盤分區(qū)
1. 修改磁盤,創(chuàng)建相應(yīng)的分區(qū)
[root@san iscsi]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 255 2048256 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 256 382 1020127+ 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/sda3 383 5221 38869267+ 5 Extended
/dev/sda5 383 395 104391 83 Linux
/dev/sda6 396 408 104391 83 Linux
/dev/sda7 409 421 104391 83 Linux
/dev/sda8 422 434 104391 83 Linux
這里創(chuàng)建了 4 個擴(kuò)展分區(qū),每個 100M 。 用 fdisk /dev/sda 創(chuàng)建的。 分區(qū)沒有格式化。
2. 使用磁盤分區(qū)生效
#partprobe
三 . 創(chuàng)建 PV
1 .相關(guān)命令
pvcreate 創(chuàng)建 PV
pvscan 掃描 PV
pvdisplay 顯示 PV
pvremove 刪除 PV
partprobe
2 .創(chuàng)建物理卷
[root@san iscsi]# pvcreate /dev/sda5 /dev/sda6
Physical volume "/dev/sda5" successfully created
Physical volume "/dev/sda6" successfully created
[root@san iscsi]# pvscan
PV /dev/sda5 lvm2 [101.94 MB]
PV /dev/sda6 lvm2 [101.94 MB]
Total: 2 [203.89 MB] / in use: 0 [0 ] / in no VG: 2 [203.89 MB]
[root@san iscsi]# pvdisplay
"/dev/sda5" is a new physical volume of "101.94 MB"
--- NEW Physical volume ---
PV Name /dev/sda5
VG Name
PV Size 101.94 MB
Allocatable NO
PE Size (KByte) 0
Total PE 0
Free PE 0
Allocated PE 0
PV UUID hDtAhK-adlx-5Ex0-ogc1-Alvm-H274-a8u7c2
"/dev/sda6" is a new physical volume of "101.94 MB"
--- NEW Physical volume ---
PV Name /dev/sda6
VG Name
PV Size 101.94 MB
Allocatable NO
PE Size (KByte) 0
Total PE 0
Free PE 0
Allocated PE 0
PV UUID Sy1wPG-XnjQ-eYD5-91vj-Ug5b-EGgU-i30lCS
四 . 創(chuàng)建 VG
1 .相關(guān)命令
vgcreate 創(chuàng)建 VG
vgscan 掃描 VG
vgdispaly
vgextend
vgreduce
vgchange
vgremove
2 .創(chuàng)建邏輯卷 VG
[root@san iscsi]# vgcreate vg0 /dev/sda5 /dev/sda6
Volume group "vg0" successfully created
[root@san iscsi]# vgscan
Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while...
Found volume group "vg0" using metadata type lvm2
Device '/dev/sda6' has been left open.
Device '/dev/sda5' has been left open.
[root@san iscsi]# vgdisplay
--- Volume group ---
VG Name vg0
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 2
Metadata Sequence No 1
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 0
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 2
Act PV 2
VG Size 200.00 MB
PE Size 4.00 MB /* 分配的塊的大小默認(rèn)為 4M*/
Total PE 50
Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0
Free PE / Size 50 / 200.00 MB
VG UUID iE7uoy-boR3-N6Cv-91Gf-G5vE-ftD6-gSGVlB
3 .刪除與添加邏輯卷
[root@san iscsi]# vgreduce vg0 /dev/sda5
Removed "/dev/sda5" from volume group "vg0"
[root@san iscsi]# vgextend vg0 /dev/sda5
Volume group "vg0" successfully extended
4. PE 和 LV 大小的關(guān)系
In order to limit the Linux kernel memory usage, there is a limit of 65,536 physical extents (PE) per logical volume (LV). Hence,
the LVM PE size will directly determine the maximum size of a logical volume (LV)!
For example,
4MB PE size (the default PE size) will limit single logical volume (LV) to 256GB, 16MB PE size will limit single LV to grow beyond 1TB,
etc.
Beside the PE size,
the maximum size of single LV is also limited by CPU architecture and Linux kernel version:
Linux kernel version 2.4.x limit the maximum LV size to 2TB.
Some older Linux kernel prior to 2.4.x, the maximum LV size is limited to 1TB (caused by the integer signedness problems in the block layer).
The combination of 32-bit CPU and Linux kernel version 2.6.x, the limit of logical volume size is maximized at 16TB.
For Linux kernel 2.6.x running on 64-bit CPU, the maximum LV size is 8EB (extremely terrible big storage for this time being!)
from :
http://www.lifelinux.com/maximum-size-of-a-logical-volume-in-lvm-6823.html
這段問題里有如下 2 個重點(diǎn)信息:
1. PE 的大小決定 LV 的容量,默認(rèn) 4M 的 PE 最大支持的 256G 的 LV 。 16M 的 PE 最大支持 1TB 的 LV 。
2. 影響 LV 容量的還有 CPU 架構(gòu)。 對于 32bit 下, Linux 內(nèi)核為 2.6.X 的支持 16TB , 64bit 下, Linux 內(nèi)核為 2.6.x 的支持 8EB 。
所以如果要想支持大量的 LV 。 那么對在創(chuàng)建 LV 的時候,還需要指定 PE 的大小。 這個我們在 vgcreate 命令中加一個 -s 參數(shù)即可:
[root@san iscsi]# vgremove vg0
Volume group "vg0" successfully removed
[root@san iscsi]# vgcreate -s 16MB vg0 /dev/sda5 /dev/sda6
Volume group "vg0" successfully created
[root@san iscsi]# vgscan
Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while...
Found volume group "vg0" using metadata type lvm2
Device '/dev/sda6' has been left open.
Device '/dev/sda5' has been left open.
[root@san iscsi]# vgdisplay
--- Volume group ---
VG Name vg0
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 2
Metadata Sequence No 1
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 0
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 2
Act PV 2
VG Size 192.00 MB
PE Size 16.00 MB - 這里我們看到 PE 改成 16MB 了。
Total PE 12
Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0
Free PE / Size 12 / 192.00 MB
VG UUID A9w4ho-3Fdo-ELYl-VRqY-yhaZ-61rt-68sXsi
五、創(chuàng)建邏輯卷 LV
1 .相關(guān)命令
lvcreate
lvscan
lvdisplay
lvextend
lvreduce
lvremove
lvresize
2 .創(chuàng)建邏輯卷 LV
[root@san iscsi]# lvcreate -L 184M -n date vg0
Rounding up size to full physical extent 192.00 MB
Logical volume "date" created
[root@san iscsi]# lvscan
ACTIVE '/dev/vg0/date' [192.00 MB] inherit
[root@san iscsi]# lvdisplay
--- Logical volume ---
LV Name /dev/vg0/date
VG Name vg0
LV UUID PAyJph-B9K2-P15u-Zkl3-pBxs-e0TG-DCuRzq
LV Write Access read/write
LV Status available
# open 0
LV Size 192.00 MB
Current LE 12 -- 注 12*16MB=192MB ,和之前的 PE 是 1:1
Segments 2
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
- currently set to 256
Block device 253:0
六、掛載邏輯卷 LV
1. lv 的格式化
[root@san vg0]# mkfs.ext3 /dev/vg0/date
mke2fs 1.40.8 (13-Mar-2008)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=1024 (log=0)
Fragment size=1024 (log=0)
49152 inodes, 196608 blocks
9830 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=1
Maximum filesystem blocks=67371008
24 block groups
8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments per group
2048 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
8193, 24577, 40961, 57345, 73729
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (4096 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 23 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[root@san vg0]# mkdir -p /u01/backup
[root@san vg0]# mount /dev/vg0/date /u01/backup
[root@san vg0]# df -T
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda1 ext3 1984016 651076 1230528 35% /
tmpfs tmpfs 349016 0 349016 0% /dev/shm
/dev/mapper/vg0-date
ext3 190403 5664 174909 4% /u01/backup
掛載成功之后,就可以使用了。
七、 LVM 的容量調(diào)整
LVM 的容量調(diào)整可以在多個環(huán)節(jié)進(jìn)行調(diào)整,比如:可以在物理卷上, VG 上,以及 LV 上,都可以進(jìn)行容量的擴(kuò)展,這也是 LVM 它的一個優(yōu)勢所在。
1 .添加物理卷 (PV)
首先應(yīng)卸載在使用過程中的 LV ,然后必須保證該磁盤的類型是 lvm 類型,才能添加進(jìn)來。
[root@san vg0]# umount /dev/mapper/vg0-date
[root@san vg0]# pvcreate /dev/sda7
Physical volume "/dev/sda7" successfully created
[root@san vg0]# pvscan
PV /dev/sda5 VG vg0 lvm2 [96.00 MB / 0 free]
PV /dev/sda6 VG vg0 lvm2 [96.00 MB / 0 free]
PV /dev/sda7 lvm2 [101.94 MB]
Total: 3 [293.94 MB] / in use: 2 [192.00 MB] / in no VG: 1 [101.94 MB]
2 .添加 VG 的容量
把上面新添加的 LVM 磁盤加入到 vg0 卷組中。
[root@san vg0]# vgextend vg0 /dev/sda7
Volume group "vg0" successfully extended
[root@san vg0]# vgdisplay
--- Volume group ---
VG Name vg0
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 3
Metadata Sequence No 3
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 1
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 3
Act PV 3
VG Size 288.00 MB
PE Size 16.00 MB
Total PE 18
Alloc PE / Size 12 / 192.00 MB
Free PE / Size 6 / 96.00 MB
VG UUID A9w4ho-3Fdo-ELYl-VRqY-yhaZ-61rt-68sXsi
3 .添加 LV 的容量
把新加入 LVM 磁盤的容量加入 LV 中。
[root@san vg0]# lvextend -L +90M /dev/vg0/date
Rounding up size to full physical extent 96.00 MB
Extending logical volume date to 288.00 MB
Logical volume date successfully resized
這里要注意,如果是 lvextend -L 90MB /dev/vg0/date , 則表示增加到 90m 。 如果有加號,就表示增加 90M 。
[root@san vg0]# lvscan
ACTIVE '/dev/vg0/date' [288.00 MB] inherit
[root@san vg0]# resize2fs -f /dev/vg0/date
resize2fs 1.40.8 (13-Mar-2008)
Resizing the filesystem on /dev/vg0/date to 294912 (1k) blocks.
The filesystem on /dev/vg0/date is now 294912 blocks long.
如果不做這一步, LV 的容量沒有真正的加入進(jìn) LV 卷中,因?yàn)橄嚓P(guān)信息寫入到了磁盤超級塊中。
4 .掛載使用
[root@san vg0]# mount /dev/vg0/date /u01/backup
[root@san vg0]# df -T
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda1 ext3 1984016 651128 1230476 35% /
tmpfs tmpfs 349016 0 349016 0% /dev/shm
/dev/mapper/vg0-date
ext3 285599 6168 267635 3% /u01/backup
八、 LVM 的卸載方法
LVM 卸載的方法與分區(qū)的刪除方法類似,就是最后創(chuàng)建的最先刪除。順序如下:
先刪除 LV
再刪除 VG
最后 PV
以前的 LVM 的分區(qū)應(yīng)用 fdisk 轉(zhuǎn)換成其它類型的文件系統(tǒng),當(dāng)普通分區(qū)使用。
九、 LVM 的卸載過程
1 . umount 取消掛載
[root@san vg0]# umount /dev/vg0/date
[root@san vg0]# df -T
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda1 ext3 1984016 651148 1230456 35% /
tmpfs tmpfs 349016 0 349016 0% /dev/shm
2 .刪除 LV 邏輯卷
[root@san vg0]# lvremove /dev/vg0/date
Do you really want to remove active logical volume "date"? [y/n]: y
Logical volume "date" successfully removed
3 .刪除 VG 卷組
[root@san vg0]# vgchange -a n vg0
0 logical volume(s) in volume group "vg0" now active
[root@san vg0]# vgremove vg0
Volume group "vg0" successfully removed
對 vgchange 命令的說明,先看幫助:
[root@san vg0]# vgchange --help
vgchange: Change volume group attributes
vgchange
[-A|--autobackup {y|n}]
[--alloc AllocationPolicy]
[-P|--partial]
[-d|--debug]
[-h|--help]
[--ignorelockingfailure]
[--ignoremonitoring]
[--monitor {y|n}]
[-t|--test]
[-u|--uuid]
[-v|--verbose]
[--version]
{-a|--available [e|l]{y|n} | - 這個是我們使用的參數(shù),表示狀態(tài)可用不可用,有兩個值: y 和 n 。
-c|--clustered {y|n} |
-x|--resizeable {y|n} |
-l|--logicalvolume MaxLogicalVolumes |
-p|--maxphysicalvolumes MaxPhysicalVolumes |
-s|--physicalextentsize PhysicalExtentSize[kKmMgGtTpPeE] |
--addtag Tag |
--deltag Tag}
[VolumeGroupName...]
4 .刪除 PV
[root@san vg0]# pvscan
PV /dev/sda5 lvm2 [101.94 MB]
PV /dev/sda6 lvm2 [101.94 MB]
PV /dev/sda7 lvm2 [101.94 MB]
Total: 3 [305.83 MB] / in use: 0 [0 ] / in no VG: 3 [305.83 MB]
[root@san vg0]# pvremove /dev/sda5 /dev/sda6 /dev/sda7
Labels on physical volume "/dev/sda5" successfully wiped
Labels on physical volume "/dev/sda6" successfully wiped
Labels on physical volume "/dev/sda7" successfully wiped
十 . 命令說明
pvcreate (創(chuàng)建物理卷)
pvdisplay ( 顯示物理卷信息)
pvscan (掃描物理卷 )
pvmove ( 轉(zhuǎn)移物理卷資料)
pvmove /dev/hda1 /dev/hda2 ( 轉(zhuǎn)移 /dev/hda1 資料到 /dev/hda2)
pvmove /dev/hda1 ( 轉(zhuǎn)到 /dev/hda1 資料到別的物理卷)
pvremove ( 刪除物理卷)
vgcreate ( 創(chuàng)建卷組 )
vgdisplay ( 顯示卷組信息 )
vgscan ( 掃描卷組 )
vgextend ( 擴(kuò)展卷組 ) vgextend vg0 /dev/hda2 (把物理卷 /dev/hda2 加到 vg0 卷組中)
vgreduce ( 刪除卷組中的物理卷) vgreduce vg0 /dev/hda2 ( 把物理卷 /dev/hda2 從卷組 vg0 中刪除 )
vgchange ( 激活卷組 ) vgchange -a y vg0 ( 激活卷組 vg0) vgchange -a n vg0 (相反)
vgremove ( 刪除卷組 ) vgremove vg0 (刪除卷組 vg0)
lvcreate ( 創(chuàng)建邏輯卷)
lvdisplay ( 顯示邏輯卷信息)
lvscan ( 掃描邏輯卷)
lvextend ( 擴(kuò)展邏輯卷) lvextend -l +5G /dev/vg0/data ( 擴(kuò)展邏輯卷 /dev/vg0/data 5 個 G )
mke2fs( 查看 LV 的 block 數(shù) ) ,如 :mke2fs -n /dev/vg0/date. 注意,這里一定要加 -n 。 這里只是查看 block 數(shù),如果不加,就把分區(qū)格式化了。 從這個命令可以得出 Block size 和 blocks ,這兩個數(shù)的乘積就是分區(qū)大小。
resize2fs( 調(diào)整文件系統(tǒng)大小 ) resize2fs -f /dev/vg0/date 剩余的 block 數(shù)
lvreduce ( 介紹 LV 大小 ) lvreduce -L-50M /dev/vg0/date ,調(diào)整 lv 分區(qū)大小,減小 50M
lvremove ( 刪除邏輯卷)
十一 . RHEL5 中 LVM 修復(fù)方法
現(xiàn)在很多人對邏輯卷不是很細(xì)心,在做邏輯卷時可能會導(dǎo)致系統(tǒng)崩潰。在此我向各位提供自己修復(fù)邏輯卷的一點(diǎn)心得。
首先說下因?yàn)檫壿嬀矶斐上到y(tǒng)癱瘓的的原因。在做邏輯卷的時候造成文件系統(tǒng)和邏輯卷的大小不統(tǒng)一而造成的系統(tǒng)癱瘓。
其實(shí)修復(fù)很簡單,但你的系統(tǒng)癱瘓后會進(jìn)入 Linux 的修復(fù)系統(tǒng)。由于進(jìn)入修復(fù)模式后所有的文件和目錄都為只讀,需要從新掛載成可讀可寫。
#mount -o remount,rw /
進(jìn)入
/etc/fstab
這個文件將需要修復(fù)的邏輯卷注釋掉。進(jìn)入系統(tǒng)進(jìn)行修改。
或者直接進(jìn)行修改:
#lvm lvexdent -L 200M /dev/vgname/lvname
#resize2fs /dev/vgname/lvname 200M
在增大或縮小 LVM 時要注意順序,這樣可以避免在對邏輯卷進(jìn)行修復(fù)。增大時先增大 LV ,后增大文件系統(tǒng),縮小時先縮小文件系統(tǒng),后縮小 LV 大小。
整理自網(wǎng)絡(luò)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware
網(wǎng)上資源: http://tianlesoftware.download.csdn.net
相關(guān)視頻: http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/archive/2009/11/27/4886500.aspx
DBA1 群: 62697716( 滿 ); DBA2 群: 62697977( 滿 )
DBA3 群: 62697850 DBA 超級群: 63306533;
聊天 群: 40132017
-- 加群需要在備注說明 Oracle 表空間和數(shù)據(jù)文件的關(guān)系,否則拒絕申請
更多文章、技術(shù)交流、商務(wù)合作、聯(lián)系博主
微信掃碼或搜索:z360901061

微信掃一掃加我為好友
QQ號聯(lián)系: 360901061
您的支持是博主寫作最大的動力,如果您喜歡我的文章,感覺我的文章對您有幫助,請用微信掃描下面二維碼支持博主2元、5元、10元、20元等您想捐的金額吧,狠狠點(diǎn)擊下面給點(diǎn)支持吧,站長非常感激您!手機(jī)微信長按不能支付解決辦法:請將微信支付二維碼保存到相冊,切換到微信,然后點(diǎn)擊微信右上角掃一掃功能,選擇支付二維碼完成支付。
【本文對您有幫助就好】元